Rhel Generate Ssh Host Keys
- SSH keys offer a highly secure manner of logging into a server with SSH as against mere dependence on a password. While a password stands the risk of being finally cracked, SSH keys are rather impossible to decipher using brute force.
- Host keys are normally generated automatically when OpenSSH is first installed or when the computer is first booted. The ssh-keygen program can be used for generating additional host keys or for replacing existing keys. Known Host Keys. SSH clients store host keys for hosts they have ever connected to.
- Quick steps: Create and use an SSH public-private key pair for Linux VMs in Azure.; 4 minutes to read +4; In this article. With a secure shell (SSH) key pair, you can create virtual machines (VMs) in Azure that use SSH keys for authentication, eliminating the need for passwords to sign in.
- How to know/find out/see my ssh host key I am using putty on a windows and managed to log in to my linux although it screamed for the unknow host key as usual for 1st time log-in. I know nothing will go wrong so I just accepted it.
- Arch Linux Generate Ssh Host Keys
- Ssh Generate Key Ubuntu
- Rhel Generate Ssh Host Key
- Rhel Generate Ssh Host Keys 2016
- Redhat Generate Ssh Host Keys
SiteGround uses key-based authentication for SSH. This has proven more secure over standard username/password authentication. More information on SSH keys can be found here. You can generate an SSH key pair directly in cPanel, or you can generate the keys yourself and just upload the public one in cPanel to use with your hosting account. Fetch public host keys. The ssh-keyscan command was developed so that users can obtain public host keys without needing to authenticate to the SSH server. From its man page: ssh-keyscan is a utility for gathering the public ssh host keys of a number of hosts. Nov 10, 2011 How to Generate A Public/Private SSH Key Linux By Damien – Posted on Nov 10, 2011 Nov 18, 2011 in Linux If you are using SSH frequently to connect to a remote host, one of the way to secure the connection is to use a public/private SSH key so no password is transmitted over the network and it can prevent against brute force attack.
ow do I regenerate OpenSSH sshd server host keys stored in /etc/ssh/ssh_host_* files? Can I safely regenerate ssh host keys using remote ssh session as my existing ssh connections shouldn’t be interrupted on Debian or Ubuntu Linux? How do I regenerate new ssh server keys? How to regenerate new host keys on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux?[donotprint][/donotprint]To regenerate keys you need to delete old files and reconfigure openssh-server. It is also safe to run following commands over remote ssh based session. Your existing session shouldn’t be interrupted.
Why regenerate new ssh server keys?
Most Linux and Unix distribution create ssh keys for you during the installation of the OpenSSH server package. But it may be useful to be able re-generate new server keys from time to time. For example, when you duplicate VM (KVM or container) which contains an installed ssh package and you need to use different keys from cloned KVM VM guest/machine.
Steps to regenerate OpenSSH host keys on Linux
Let us see all steps
Step 1 – Delete old ssh host keys
Login as the root and type the following command to delete files on your SSHD server:# /bin/rm -v /etc/ssh/ssh_host_*
Sample outputs:
Step 2 – Debian or Ubuntu Linux Regenerate OpenSSH Host Keys
Now create a new set of keys on your SSHD server, enter:# dpkg-reconfigure openssh-server
Sample output:
You just regenerated new ssh server keys. You need to restart ssh server:$ sudo systemctl restart ssh
OR$ /etc/init.d/ssh restart
Step 3 – Update all ssh client(s) known_hosts files
Finally, you need to update ~/.ssh/known_hosts files on client computers, otherwise everyone will see an error message that read as follows:
Either remove host fingerprint or update the file using vi text editor (command must be typed on client machine):$ ssh-keygen -R remote-server-name-here
Now login using the ssh command:$ ssh vivek@server1.cyberciti.biz
Arch Linux Generate Ssh Host Keys
Conclusion
You just regenerated OpenSSH Host Keys on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux using the dpkg-reconfigure command. For more info see the man page or this wiki page here:$ man dpkg-reconfigure
$ man sshd
ADVERTISEMENTS
Introduction – SSH is an acronym for secure shell. It is a suite of cryptographic network protocol. It allows users to log in and transfer files securely over the unsecure network such as the Internet. OpenSSH is an implementation of SSH protocol on RHEL 8. You can log in using RHEL 8 user and password account. However, OpenSSH project recommends log in using a combination of a private and public SSH keys.
Sample set up for our RHEL 8 server
/delphi-howto-generate-api-key.html.
Where,
- You generate a key pair on your Linux/Unix/macOS desktop.
- Place the public key on RHEL 8 server.
- One can unlock public key using a private key stored on your desktop with the help of ssh command.
- When both the public and private key correct you can log in without a password.
How do I set up SSH keys on RHEL 8 server?
The procedure to set up SSH key on Red Hat Enteprise Linux 8 server:
Ssh Generate Key Ubuntu
- On your local desktop type:
ssh-keygen - Install public key into remote RHEL 8 server using:
ssh-copy-id user@remote-RHEL8-server-ip - Use ssh for password less login:
ssh user@remote-RHEL8-server-ip
Let us see all commands and steps in details.
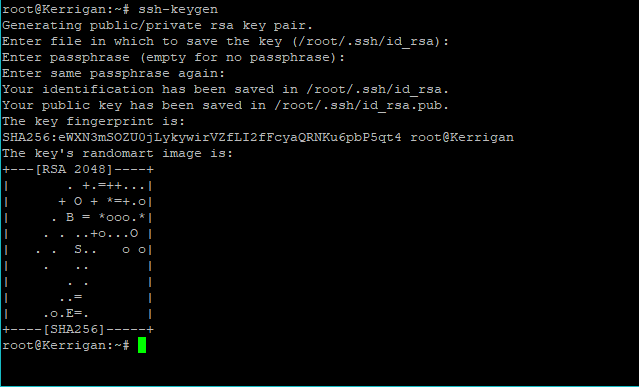
How to create the ed25519 or RSA key pair
The syntax is:ssh-keygen -t ed25519
ssh-keygen -t rsa
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f ~/.ssh/aws-lighsail.key -C 'My AWS SSH Keys'
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f ~/.ssh/linode-usa-www1-vps.key -C 'My Linode SSH Keys for www'
Where,
- -t rsa OR -t ed25519 : Specifies the type of key to create. The possible values “dsa”, “ecdsa”, “ed25519”, or “rsa” for SSH protocol version 2.
- -b 4096 : Specifies the number of bits in the key to create.
- -f~/.ssh/aws-lighsail.key : Specifies the filename of the key file.
- -C -C 'My AWS SSH Keys' : Set a new comment.
I am going type the following command on my Ubuntu desktop to create the key pair:$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519
I strongly recommend that you set up a passphrase when prompted.
How to copy the public key
Now our key paid generated and stored in ~/.ssh/ directory. You must copy a public SSH key file named ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub (or ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub if you created RSA key) to the RHEL 8 server. Try the ssh-copy-id command as follows:$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/fileNameHere.pubuser@remote-RHEL8-server-ip
For example:$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub vivek@192.168.2.211
Rhel Generate Ssh Host Key
How to log in using ssh and without a password
Now try logging into the machine, with the ssh command as follows:$ ssh user@rhel-8-server
$ ssh vivek@192.168.2.211
You should be able to log in without a password. If you set up a passphrase, unlock it as follows for your current session so that you don’t have to enter it every time you run ssh, sftp, scp, rsync and other commands:$ ssh-agent $SHELL
$ ssh-add
Optional settings for root user
Word generation series 1-assessement answer key. Disable root user log in all together on RHEL 8 via ssh. Log in as root user on RHEL 8 and run following to add a user named vivek to wheel group:# usermod -aG wheel vivek
# id vivek
Allows users in group wheel can use sudo command to run all commands on RHEL 8 server. Next disable root user login by adding the following line to sshd_config:# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Disable the password for root login and only allow ssh keys based login:
Rhel Generate Ssh Host Keys 2016
Save and close the file. Reload the ssh server:# systemctl reload sshd.service
For more info see “Top 20 OpenSSH Server Best Security Practices“.
Conclusion
You learned how to set up and use SSH keys to manage your RHEL 8 based server. For more info see OpenSSH man pages here.
Redhat Generate Ssh Host Keys
ADVERTISEMENTS